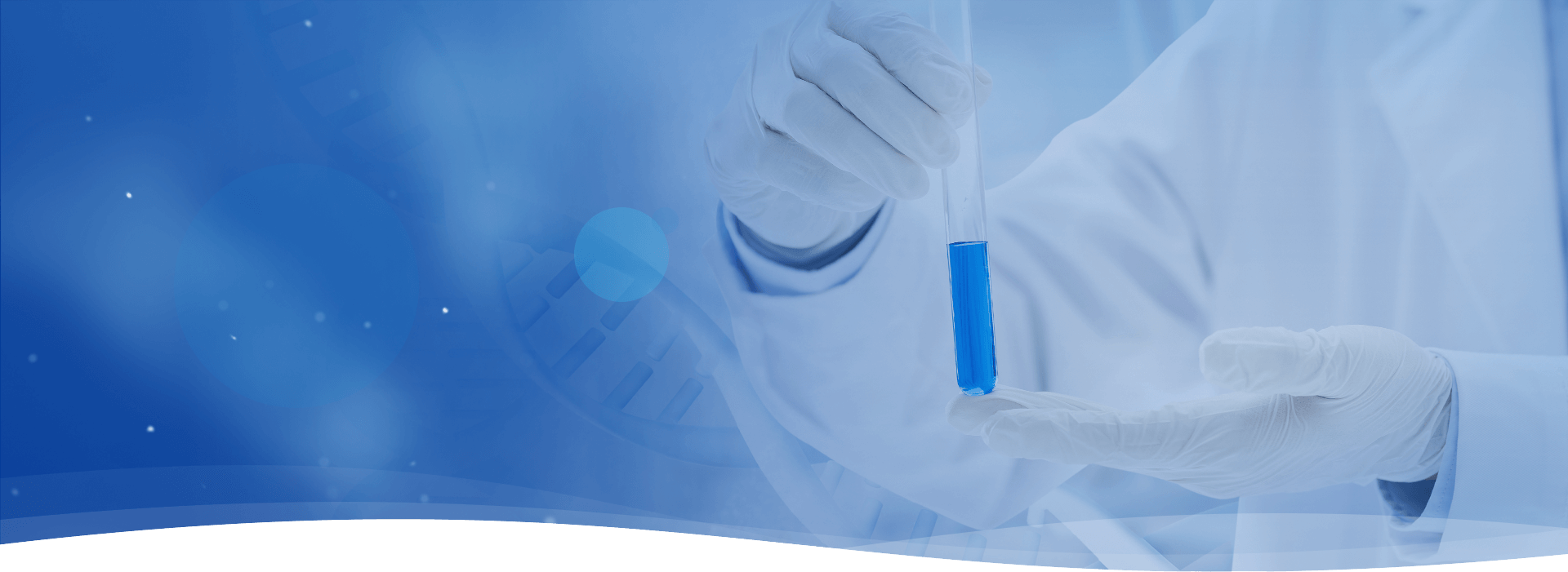
Use HPV DNA test for Preliminary Screening!
![]() 0
0
![]() 2021-07-08
2021-07-08
In 2020, it is estimated that there will be more than 600,000 new cases of cervical cancer in the world, and more than 340,000 women will die from cervical cancer, while the number of new cases of cervical cancer announced by ICO/IARC in 2019 is 570,000 and 310,000 deaths. Cervical cancer Threats to the health of women around the world continue to increase.
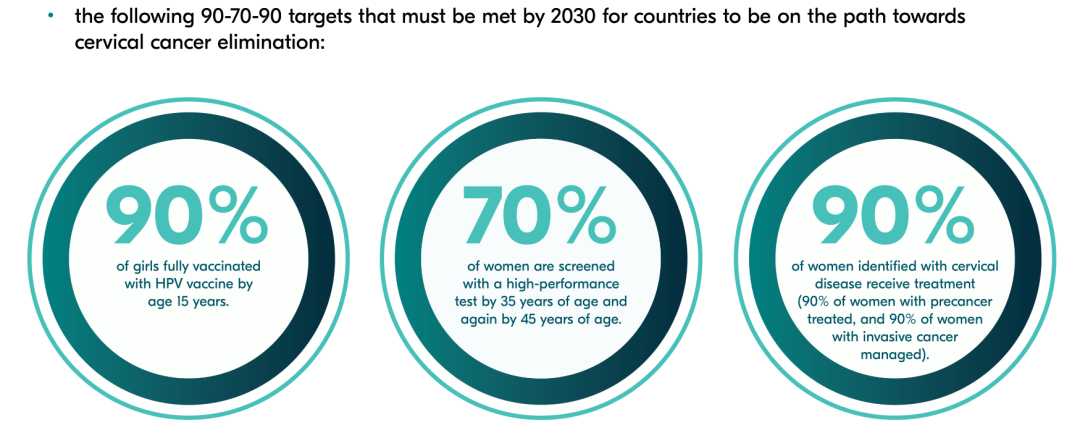
In 2020, WHO launched the "Global Strategy to Accelerate Cervical Cancer Elimination" and set the following goals by 2030:
- 90% of girls are fully vaccinated with the HPV vaccine by the age 15 years.
- 70% of women are screened with a high-performance test y 35 years of age and again by 45 years of age.
- 90% of women identified with the cervical disease receive treatment (90% of women with precancer treatment, and 90% of women with invasive cancer managed)
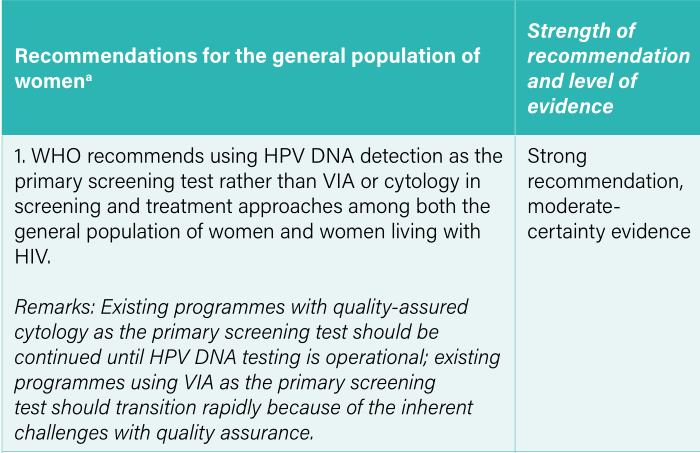
- In previous WHO document didn't specify what is an efficient detection method. But the WHO recently released the
, which clarified HPV DNA testing as a primary screening method and defined it as an efficient method.

Differences between these two screening guideline
| First Edition | Second Edition | |
|---|---|---|
| Issued Year | 2013 | 2021 |
| Primary Screening Suggestion | Use VIA or cytology for primary screening, HPV testing is only recommended in well-resourced areas | HPV DNA testing is recommended as the primary screening method, and areas that use VIA primary screening are recommended to switch to HPV DNA testing as soon as possible, and areas that use cytology (guaranteed quality control) primary screening can continue before the implementation of the HPV DNA testing primary screening program |
After 8 years, the guidelines are updated because HPV DNA testing is an objective result, unlike methods that rely on visual inspection, and there is sufficient evidence from clinical studies that HPV DNA testing has better screening sensitivity and specificity.
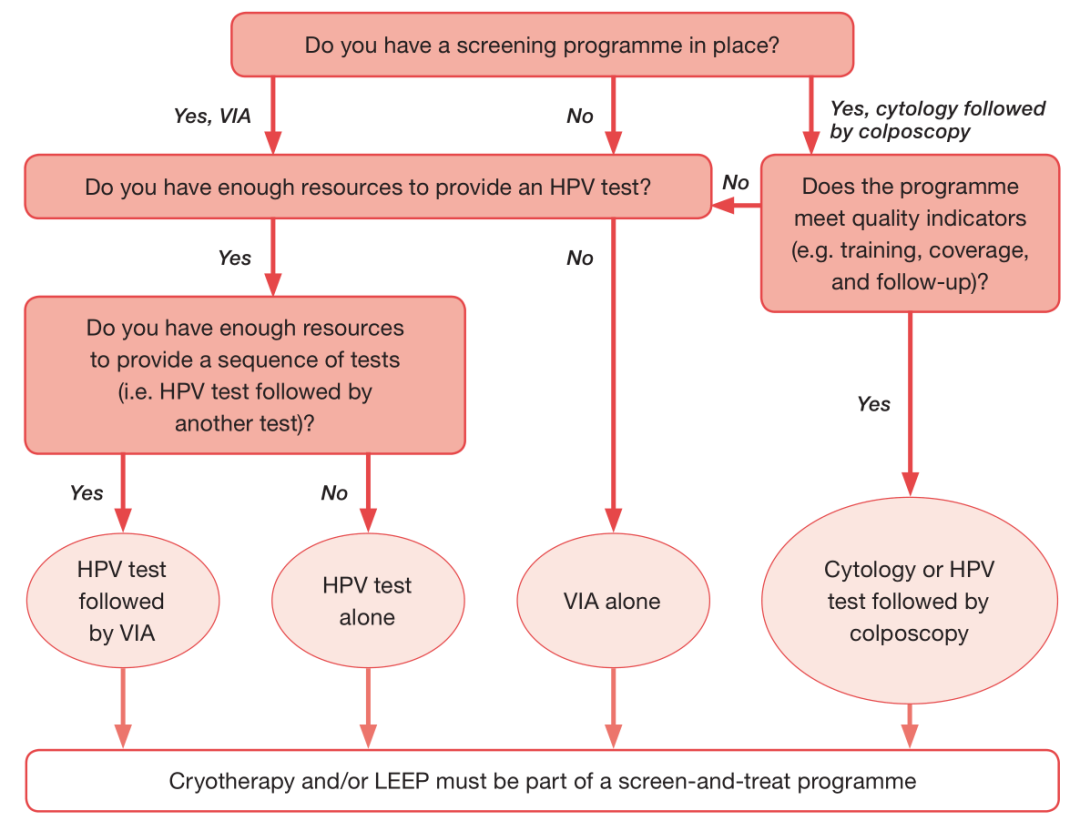
14 New Criteria
The Guidelines recommend that the average woman should be tested for HPV DNA from the age of 30, with regular screening every 5-10 years. Regarding screening methods, frequencies, and related treatments, specific recommendations, and management practices state the following:- HPV DNA testing is recommended as a primary screening method in screening and treatment approaches.
- Regardless of whether a triage strategy is used, HPV DNA testing is the primary screening method of choice.
- In a "screen-and-treat" strategy, treatment is recommended for women who test positive for HPV DNA. In the "screen, triage, and treat" strategy, triage by genotyping, colposcopy, VIA, or cytology is recommended for women who test positive for HPV DNA.
- For HPV DNA testing, the sample can be collected by a health care professional or by the woman herself. Self-sampling may be more comfortable for patients, but professional guidance is required.
- The average woman starts regular cervical cancer screening at the age of 30.
- After the age of 50, screening can be discontinued if regular screening at the WHO-recommended screening interval and two consecutive negative results.
- The average female aged 30-49 years should be screened first. Preference should also be given to women who have never been screened in the 50-65-year-old female age group when appropriate care is available.
- If using HPV DNA testing as the main screening method, the regular screening interval is 5-10 years.
- If HPV DNA testing has not been implemented and VIA or cytology is still used as the primary screening method, periodic screening is required every 3 years.
- Screening even twice in a lifetime is beneficial.
- If the initial screening of HPV DNA is positive and the triage test is negative, the HPV DNA test will be repeated after 24 months, and if it is negative, it can be switched to regular screening intervals.
- If the initial cytology screening is positive, but the colposcopy results are normal, the HPV DNA test should be repeated at 12 months, and if negative, it can be switched to regular screening intervals.
- HPV DNA test review after 12 months is preferred for histological diagnosis of CIN2/3, adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS), or due to positive screening results, and if negative, it can be switched to regular screening intervals.
- An institution can provide HPV DNA testing for the next routine screening, regardless of how women were previously screened. If screening is currently using cytology or VIA, continue until HPV DNA testing is available.